The production of metal steel pipes is carried out using admixtures of non-ferrous metals. The cross-section of metal pipes can be, usually, round, rectangular, square, but they also produce steel pipes with oval and other sections.
Classifications of steel pipes
Classes
- First and second class – carbon steel pipes, used when there are no special requirements, eg, in the manufacture of scaffolding, fencing and so on. They are also used for local distribution of liquid and gaseous substances.
- Third class – used in systems operating under pressure and at high temperatures.
- Fourth grade – used for searching and exploiting oil fields.
- Fifth grade – used in the production of transport equipment: carriage building, automotive industry and so on, in steel structures: masts, supports, etc. and as furniture elements.
- Sixth grade – used to make pump pistons and cylinders, shafts and other machine parts.
Profile, cast and special purpose.
There are not many differences between steel pipes, since they are all made of steel. According to manufacturing technology, steel pipes are divided into:
- Pipes, which are made by smelting in specialized mechanical furnaces – cast pipes. This group includes galvanized and non-galvanized water and gas pipes. They can be produced either with chopped, and rolled thread. Stainless steel galvanized pipes are widely used. Their main advantage is increased corrosion resistance to external influences.. They are used when installing gas, water pipes, as well as heating systems.
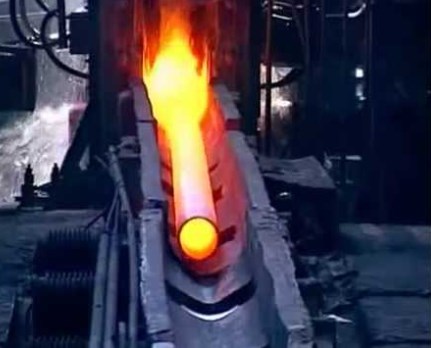
Pipe casting machines are used in the production of cast steel pipes. - Pipes, which are made using special blanks, formed and welded at the joints – welded pipes. Welded steel pipes are made from rolled sheets by welding. They are produced by electric welding, using carbon or low alloy steel, used in mechanical engineering. Welded pipes have manufacturing differences among themselves, There are electric-welded and cold-deformed pipes. The cost of these pipes depends on the technology used. Welded pipes are used in the installation of various pipelines. Electric welded pipes are divided into the following types:
-
- Pipes, having rectangular and square cross-section;
- Round and oval.
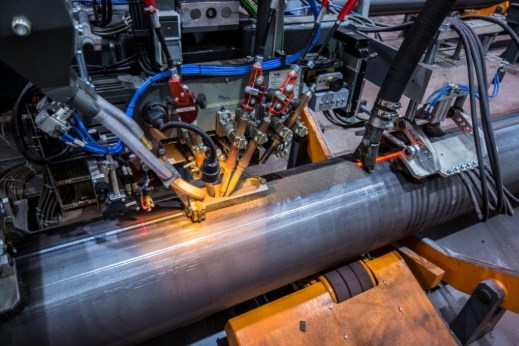
-
- Pipes, which differ from welded pipes, that are made by other drawing methods, pressing and rolling of pipe blanks – seamless pipes. Seamless pipes are divided into cold-deformed and hot-deformed. They are available in sizes from 20-550 mm. Cold-formed steel pipes are particularly thin-walled(0,3-6 mm), thin-walled and thick-walled (2-12 mm). The role of seamless pipes in building structures is very important. The design of these pipes is reliable and durable.
Classification by nomenclature
Classification of pipes according to nomenclature occurs in the following way:
- Profile pipes can have a square, oval, rectangular or flat oval shape.
- Pipes for special purposes can be welded or hot-deformed.
- Cast pipes or pipes made of ferrous metal are steel and cast iron.
- Pipes, There are pump and compressor pipes intended for the operational needs of wells, exploration pipes, drill pipes and casing.
The entire range and classification of pipes is described in State Standards. According to GOST, the dimensions of steel pipes and the quality of steel are also determined, from which pipes are made. Steel pipes are recognized by markings, applied to them. All names and names of existing markings for steel pipes can also be found in State Standards. After this you should have no problems with technical names.
Steel pipes from RT Steel
You can buy steel pipes here, at RT Steel. This is a successful Ekaterinburg company, engaged in the sale and delivery of steel goods (stainless, black, galvanized) like a railway, and by road transport throughout Russia.
The use of steel pipes is very wide in various fields, and it depends on their cross-section and parameters. These metal products are most used, in such industries, as:
- In the production of heating systems, when laying pipelines, as well as in the installation of gas supply, drainage and sewerage.
- In the manufacture and construction of enclosing structures.
- For oil transportation, gas and chemicals under pressure.
- In the mining industry (casings and wells).
- For the manufacture of complex and simple metal structures.
- Irrigation system equipment (water supply and distribution).
- Oil industry (development and exploration of deposits).







